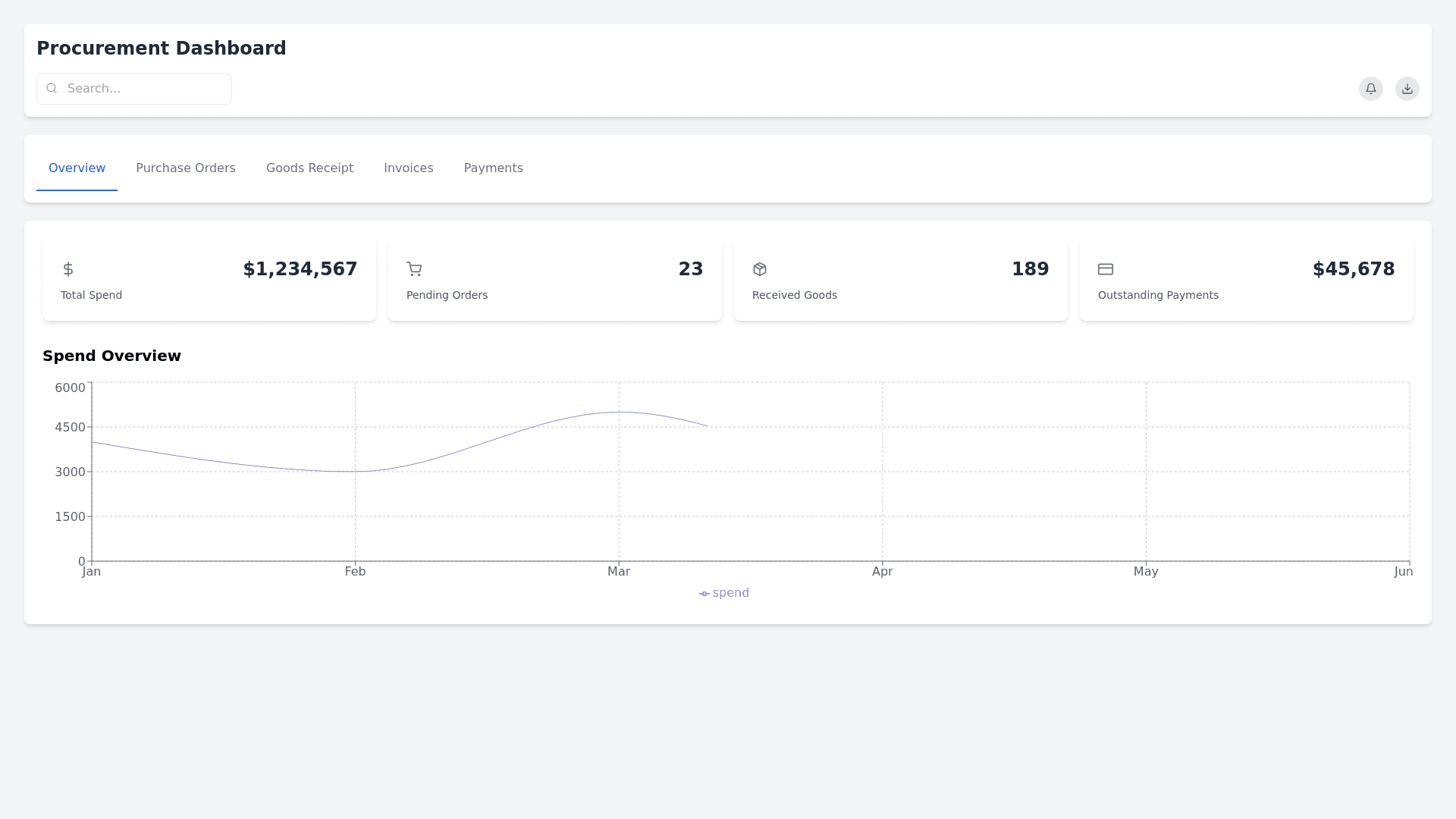
Procurement Dashboard - Copy this React, Tailwind Component to your project
1. Procurement & Purchase Orders (PO) Process: The procurement department places orders for raw materials, machinery, and other necessary goods. A Purchase Order (PO) is created and sent to suppliers, detailing quantities, prices, and delivery terms. Accounting Entry: No accounting entry is made yet. The PO is a commitment to spend, not an actual financial transaction. 2. Receiving Goods (Goods Receipt) Process: Upon receiving the ordered goods or services, the company checks the quality and quantity. A Goods Receipt Note (GRN) is generated to confirm that the materials have been received as ordered. Accounting Entry: Still no direct accounting entry, but the inventory system is updated to reflect the received goods. Debit: Raw Materials Inventory Credit: GRN Suspense Account (Not yet payable to the supplier until the invoice arrives) 3. Supplier Invoice Received Process: The supplier sends an Invoice after delivery. The invoice is matched against the PO and the GRN to ensure consistency in terms of quantity, price, and terms. Accounting Entry: Debit: Raw Materials Inventory (If goods are for production) Credit: Accounts Payable (Liability to supplier) 4. Payment to Supplier Process: Payment is made based on the terms (e.g., 30 days). The payment process involves bank authorization, and finally, the payment is settled. Accounting Entry: Debit: Accounts Payable Credit: Bank/Cash (Reduction in cash/bank balance) 5. Production Process (Cost Accounting) Process: Raw materials are consumed in the manufacturing process. Labor and overhead costs are also allocated to the production. Accounting Entries: Debit: Work in Progress (WIP) Inventory (The value of raw materials, labor, and overheads used) Credit: Raw Materials Inventory (For materials consumed) Debit: Factory Overhead (For overhead costs like utilities) Credit: Various accounts (e.g., Accounts Payable, Salaries Payable) 6. Completion of Production (Finished Goods) Process: Once the production is complete, the costs associated with production are transferred to Finished Goods Inventory. Accounting Entries: Debit: Finished Goods Inventory Credit: Work in Progress (WIP) Inventory 7. Sales Order (Customer Invoice) Process: When a customer places an order, a Sales Order (SO) is generated. Once goods are shipped or delivered, a customer Invoice is issued. Accounting Entry: Debit: Accounts Receivable (Receivable from the customer) Credit: Sales Revenue (Revenue from the sale) Debit: Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) (Cost of the finished goods) Credit: Finished Goods Inventory (Reduce inventory) 8. Customer Payment Received Process: The customer makes payment within the credit terms agreed upon (e.g., 30 days). Accounting Entry: Debit: Bank/Cash Credit: Accounts Receivable (Reduction in receivables) 9. General Ledger & Month End Close Process: At the end of the month, the accounting department performs a month end close by consolidating all financial transactions. Adjustments, accruals, and amortization entries are made to reflect true financial performance and position. Accounting Entries: Adjustments like depreciation, accrued expenses, and other necessary entries are recorded. Examples: Debit: Depreciation Expense Credit: Accumulated Depreciation Accruals: Debit: Expenses Credit: Accrued Liabilities 10. Financial Reporting Process: The financial statements, including the Income Statement (Profit & Loss), Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement, are generated based on accounting data. Key Reports: Income Statement shows profitability. Balance Sheet shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Cash Flow Statement tracks the inflows and outflows of cash. generate a dashboard